CLUB MOSSES
The club mosses are small, creeping, plants, which lack flowers and reproduce sexually by
spores and has horizontal underground stem( Rhizome)
The
sporophyte consists of true
roots, an
aerial stem and scale-like
leaves
. These are small and spirally arranged on an elongated stem.
Terminal cluster of leaves called strobilli that are club shaped and bear sporangia

Lycopodium d
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Horse tails
Equisetaceae, a family of Vascular plants that reproduce by Spores rather than seeds.
the stems are coated with abrasive , Silicates making them useful for (cleaning) metal items such as cooking pots or drinking mugs,
If eaten in large quantities, the foliage of some species is Poison to grazing animals
plants the Leaves are greatly reduced and usually nonPhoto synthetic

=====================
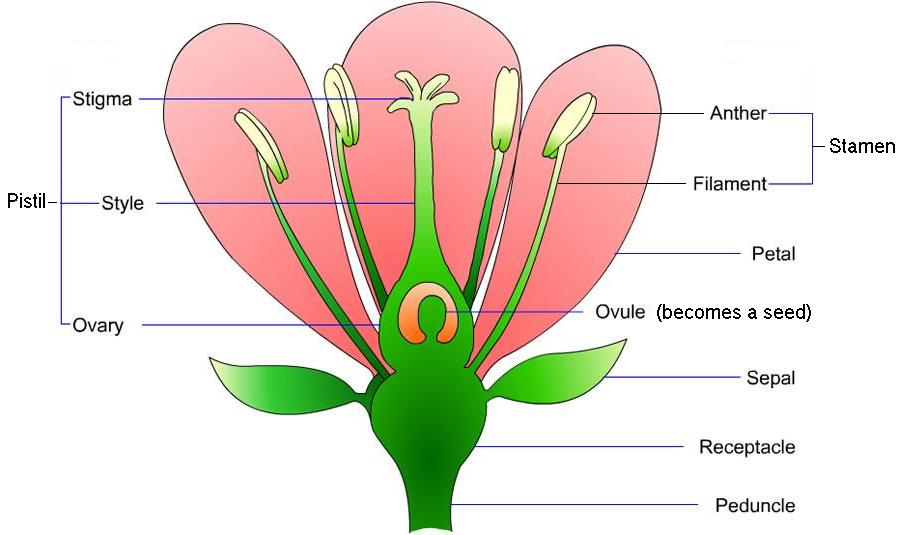
Lilium Ovary
![[lily megasporocyte in ovule]](http://faculty.baruch.cuny.edu/jwahlert/bio1003/images/anthophyta/megasporocyte.jpg) Lilium ovary:
Lilium ovary:
contains several ovules.
each ovary contans diploid megaspore mother cell in a chamber called the megasporangium.
Tissue called integuments, surround the megasporangium;
The integuments will eventually become the seed coat.
=================================================================
Lilium anthers
microspore divides by mitosis to form a male gametophyte or pollen grain.
Pollen can be transported by wind (grasses usually), insects (most of the colorful flowers), and by night flying moths and small mammals (bats and mice).
![[anther microsporangia]](http://faculty.baruch.cuny.edu/jwahlert/bio1003/images/anthophyta/anther_1.jpg)
![[anther microsporangium]](http://faculty.baruch.cuny.edu/jwahlert/bio1003/images/anthophyta/anther_2.jpg)
=====================================================================
Class Monocotyledoneae: Monocots
Flower parts in 3's or multiple of 3's; one cotyledon inside seed; parallel leaf venation; includes Lilium, Amaryllis, Iris, Agave, Yucca, orchids, duckweeds, annual grasses, bamboos and palms
======================================================================
Class Dicotyledoneae: Dicots
Flower parts in 4's or 5's; 2 cotyledons inside seed; branched or net leaf venation; contains the most species of flowering herbs, shrubs and trees; includes roses (Rosa), buttercups (Ranunculus), clover (Trifolium), maple (Acer), basswood (Tilia),
==================================================================
Gymnosperms: Plants With Naked Seeds
Gymnosperms include pines (Pinus), spruce (Picea), fir (Abies), hemlock (Tsuga) and false hemlock (Pseudotsuga). Some of the coniferous genera (division Coniferophyta) are the most important timber trees in the world. Since these species have several cotyledons inside their seeds, they are conveniently referred to as polycots.
==========================================================================
Vascular plants contain two main types of conduction tissue, the xylem and phloem
extend from the leaves to the roots, and are vital conduits for water and nutrient transport. In a sense, they are to plants what veins and arteries are to animals.
Xylem tissue conducts water and mineral nutrients from the soil upward in plant roots and stems.
Phloem tissue conducts carbohydrates manufactured in the leaves downward in plant stems.
===========================
Anatomy Of Monocot Stems
Monocot stems, such as corn, palms and bamboos, do not have a vascular cambium and do not exhibit secondary growth by the production of concentric annual rings.
They cannot increase in girth by adding lateral layers of cells as in conifers and woody dicots. Instead, they have scattered vascular bundles composed of xylem and phloem tissue
The following illustrations and photos show scattered vascular bundles in the stem cross sections of corn (Zea mays):

==============================================
dicot roots, the xylem tissue appears like a 3-pronged or 4-pronged star.
The tissue between the prongs of the star is phloem.
The central xylem and phloem is surrounded by an endodermis, and the entire central structure is called a stele.

========================================
(Tilia americana), a typical ring-porous hardwood of the eastern United States:

=======================================================================
| MONOCOTS |
DICOTS |
| Embryo with single cotyledon |
Embryo with two cotyledons |
| Pollen with single furrow or pore |
Pollen with three furrows or pores |
| Flower parts in multiples of three |
Flower parts in multiples of four or five |
| Major leaf veins parallel |
Major leaf veins reticulated |
| Stem vacular bundles scattered |
Stem vascular bundles in a ring |
| Roots are adventitious |
Roots develop from radicle |
| Secondary growth absent |
Secondary growth often present |
===========================================================
Helianthis Dicot stem

======================================================
Tilia Stem

======================================================================
Zea Stem

======================================================================
Syringa Leaf
The palisade mesophyll produces carbohydrates by photosynthesis. The spongy mesophyll below has numerous air spaces to allow gas exchange between the mesophyll and the outside air via the stomata. The upper and lower cuticle protect the leaf from water, sealing water inside and preventing excess rainwater from entering. The upper and lower epidermis produce the cuticle and protect the leaf from herbivores and parasites. The xylem transports water into the leaf while the phloem begins the sugar transport down to the roots. The guard cells open and close the stoma, which is the small air space between them

-----------
Difference between gymnosperm and angiosperms
1. The angiosperms are seed bearing plants whose seeds are contained in an ovary inside a fruit. The gymnosperms are those whose seeds are exposed and not enclosed in an ovule.
2. The angiosperms are those plants that have triploid tissues while the gymnosperms have haploid.
3. The leaves of the angiosperms are flat while those of the gymnosperms are cone bearing or needle like.
4. The gymnosperms are known as softwood as they have the ability to last during the winter while the angiosperms are known as hardwood and usually changes color during and die.
2.
The following table describes the major types of fruits:
|
Simple Fruits
(derived from a single ovary)
|
Pericarp Fleshy
|
Pericarp Indehiscent
(does not split open when ripe)
|
Pericarp Dehiscent
(splits open when ripe)
|
|
Drupe, Pome, Berry, Pepo
|
Akene, Nut, Caryopsis
|
Legume, Silique, Capsule, Follicle
|
|
Multiple Fruit
(derived from the varies of several flowers united into a single mass)
|
Strawberry, Blackberry, Raspberry
|
|
Aggregate Fruit
(derived from numerous ovaries of a single flower that are scattered over a single receptacle and later unite to form a single fruit)
|
Pineapple
|